Application of Germanium in Infrared Detectors
Basic Characteristics of Germanium
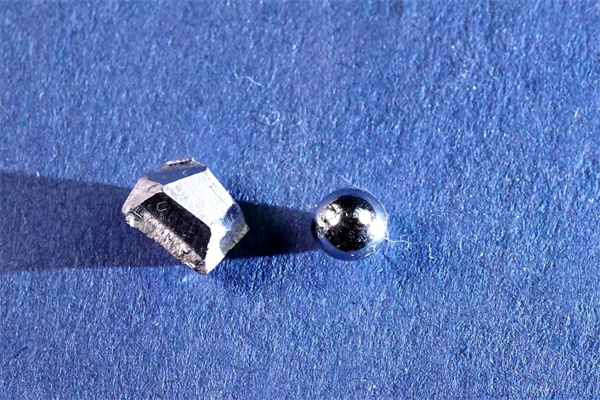
Germanium (Ge), a rare and scattered metallic element, is located in Group IVA of the periodic table with an atomic number of 32 and an atomic weight of 72.59. It is renowned for its silvery-gray, brittle metallic appearance, high melting point of 937.4°C, and boiling point of 2830°C. At a temperature of 125°C, germanium has a density of 5.323g/cm³ and a Mohs hardness of 6.3. These physical properties make germanium an ideal semiconductor material widely used in various high-tech fields. Principles and Applications of Infrared Detectors
An infrared detector is a device capable of detecting infrared radiation, operating based on the principles of infrared absorption and conversion. Such devices have broad applications in military, security, medical, and other fields. By accurately measuring changes in infrared intensity, infrared detectors can help us identify distant heat sources, monitor ambient temperature changes, and even be used for disease diagnosis in the medical field.
Core Role of Germanium in Infrared Detectors
Principles and Applications of Infrared Detectors
An infrared detector is a device capable of detecting infrared radiation, operating based on the principles of infrared absorption and conversion. Such devices have broad applications in military, security, medical, and other fields. By accurately measuring changes in infrared intensity, infrared detectors can help us identify distant heat sources, monitor ambient temperature changes, and even be used for disease diagnosis in the medical field.
Core Role of Germanium in Infrared Detectors Due to its excellent infrared photoelectric properties, germanium has become one of the ideal core materials for manufacturing infrared detectors. By doping and precision processing germanium, high-sensitivity and high-resolution infrared detectors can be fabricated. Specifically, doping germanium can significantly alter its electronic properties, thereby enhancing the detector's response speed and sensitivity. Meanwhile, precision processing helps optimize the detector's structure, further improving its performance and reliability.
Role of Doping Technology
The application of doping technology in germanium is a crucial step in achieving its superior infrared photoelectric properties. By introducing specific impurity elements into germanium, its electronic energy level structure can be adjusted, thus improving germanium's absorption capacity for infrared radiation and photoelectric conversion efficiency. For example, doping with appropriate amounts of arsenic or phosphorus can significantly enhance the response sensitivity of germanium-based infrared detectors in the short-wave infrared region.
Due to its excellent infrared photoelectric properties, germanium has become one of the ideal core materials for manufacturing infrared detectors. By doping and precision processing germanium, high-sensitivity and high-resolution infrared detectors can be fabricated. Specifically, doping germanium can significantly alter its electronic properties, thereby enhancing the detector's response speed and sensitivity. Meanwhile, precision processing helps optimize the detector's structure, further improving its performance and reliability.
Role of Doping Technology
The application of doping technology in germanium is a crucial step in achieving its superior infrared photoelectric properties. By introducing specific impurity elements into germanium, its electronic energy level structure can be adjusted, thus improving germanium's absorption capacity for infrared radiation and photoelectric conversion efficiency. For example, doping with appropriate amounts of arsenic or phosphorus can significantly enhance the response sensitivity of germanium-based infrared detectors in the short-wave infrared region. Impact of Processing Technology
Precision processing involves not only the control of material shape and size but also surface treatment and microstructural design. By precision polishing and grinding germanium, the surface smoothness and optical performance of the detector can be optimized to their best state. Additionally, adopting advanced nanoprocessing techniques can form nano-scale structures on the germanium surface, further increasing its absorption area for infrared radiation and improving detection resolution.
Impact of Processing Technology
Precision processing involves not only the control of material shape and size but also surface treatment and microstructural design. By precision polishing and grinding germanium, the surface smoothness and optical performance of the detector can be optimized to their best state. Additionally, adopting advanced nanoprocessing techniques can form nano-scale structures on the germanium surface, further increasing its absorption area for infrared radiation and improving detection resolution.